About the JFT-Basic
1. Objective of the Test
The Japan Foundation Test for Basic Japanese (JFT-Basic) seeks to measure the level of Japanese language proficiency needed by foreign nationals about to reside in Japan mainly for work, to communicate in everyday life situations. It is used to assess whether they have the Japanese language proficiency to be able to engage in everyday conversation to a certain extent and handle daily life without difficulties. The test evaluates Japanese language competence based on the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, teaching, assessment (CEFR) and the JF Standard for Japanese-Language Education![]() , a framework for Japanese language education grounded on the principle of using the Japanese language to facilitate mutual understanding among people. (The JF standard was developed based on the concepts supporting the CEFR by the Japan Foundation.)
, a framework for Japanese language education grounded on the principle of using the Japanese language to facilitate mutual understanding among people. (The JF standard was developed based on the concepts supporting the CEFR by the Japan Foundation.)
The JFT-Basic is also used as a test to measure the level of Japanese language proficiency needed to obtain the residency status of “Specified Skilled Worker (i),” which began in April 1, 2019. Please visit the following for more information on Specified Skill eligibility.
2. Target of the Test
This test is for foreign nationals who are not native speakers of Japanese.
In particular, it is aimed at foreign nationals about to reside in Japan mainly for work.
3. Testing Method
This test is conducted through Computer-Based Testing (CBT). Questions are set and answered on computers at test centers in each country. In booths, test-takers answer on the computer screen based on questions displayed on the screen and audio played through the headphones.
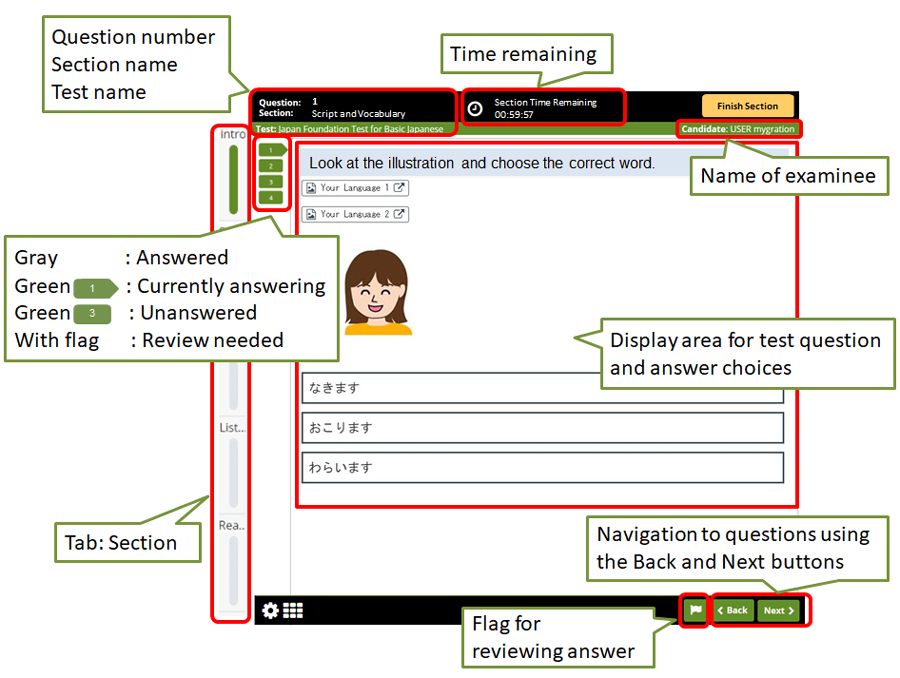
The test questions and choices are displayed on the central area of the computer screen. In addition, the section name, test name, time remaining and status of answers are displayed on the borders of the screen.
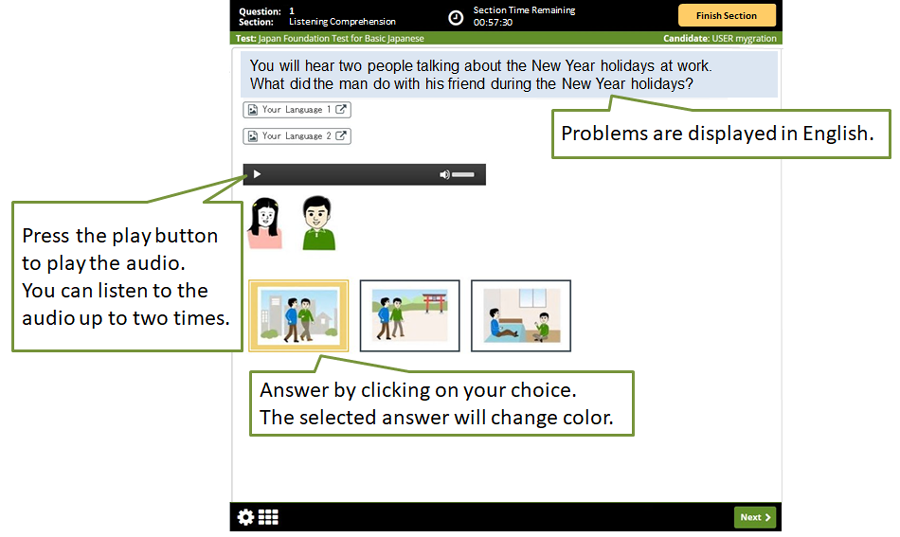
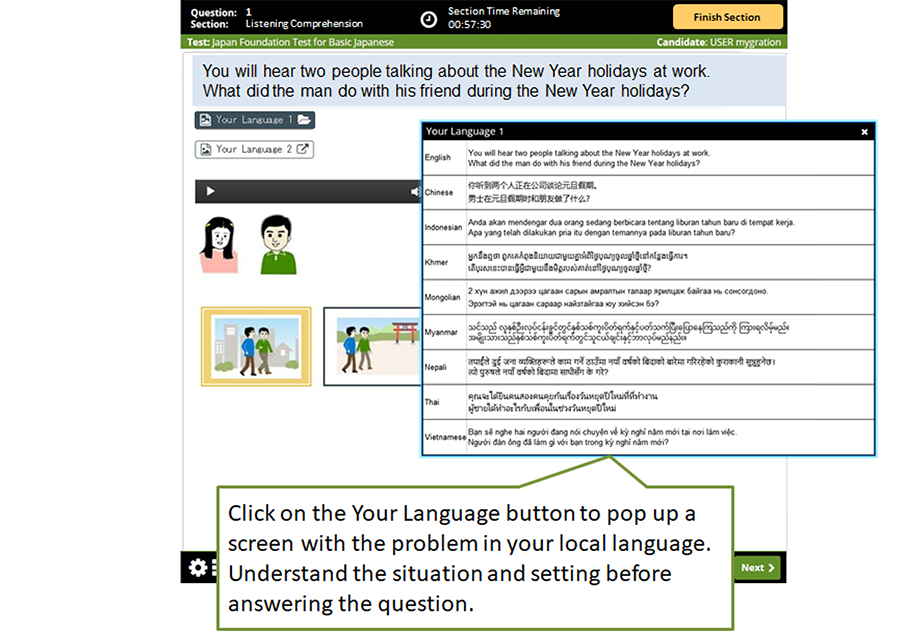
In the test, problems are displayed in English. Problems can be read in your local language* by clicking on the Your Language button.**
Read the problem to understand the setting or situation and answer the question. For listening comprehension, press the play button to play the audio playback. You can listen to the audio up to two times. To answer, click on your choice. The color of your selected choice will change.
*“Your local language” is as follows:
Your Language 1: English, Chinese, Indonesian, Khmer, Mongolian, Myanmar, Nepali, Thai, or Vietnamese
Your Language 2: Uzbek, Bengali, Lao or Malay
**The Question and Pop-up of the problem in local language may be displayed side by side depending on the screen size of the computer.
- [Related information]
- To learn more about how to operate the test screen, please refer to this link.
4. Test Structure
This test is composed of four sections: Script and Vocabulary, Conversation and Expression, Listening Comprehension, and Reading Comprehension. The purposes of this test structure and questions are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Test Structure and Purposes
| Section | Purposes of the section | Category | Purpose of category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Script and Vocabulary ( Around 12 questions) |
To test if the test-taker is able to read Japanese texts used in everyday situations, and whether the test-taker has the basic vocabulary and is able to use it. | Word meaning | To test the meaning of a word. |
| Word usage | To test the usage of a word. | ||
| Kanji reading | To test the hiragana pronunciation of a word written in kanji. | ||
| Kanji meaning and usage | To test the meaning and usage of a word written in kanji. | ||
| Conversation and Expression ( Around 12 questions) |
To test if the test-taker is able to use the grammar and expressions necessary for conversation in everyday situations. | Grammar | To test if the test-taker can use the appropriate grammar matching the context. |
| Expression | To test if the test-taker is able to use the appropriate expression matching the context. | ||
| Listening Comprehension ( Around 12 questions) |
To test if the test-taker is able to listen to and understand conversations, instructions, etc. in everyday situations. | Comprehending content (conversation) | To test understanding of contents by listening to an exchange of information or social exchange. |
| Comprehending content (communicating at shops and public places) | To test understanding of contents by listening to an exchange at a shop or public place. | ||
| Comprehending content (listening to announcements and instructions) | To test understanding of contents by listening to instructions and announcements, audio media, etc. | ||
| Reading Comprehension ( Around 12 questions) |
To test if the test-taker is able to read and understand letters, notices, explanations, etc. in everyday situations. | Comprehending content | To test reading of a short and simple letter, message, etc. |
| Information search | To test if the test-taker is able to find the necessary information from an everyday billboard, notice, information material, etc. |
There are approximately 50 questions, and the test time is 60 minutes. There is no time limit for completing each section. You can review and answer again at any time as long as you are within the same section. However, once you move to the next section, you cannot go back to the previous section. In the Listening Comprehension section, you cannot go to the previous or next question to review and answer again.
5. Summary of Linguistic Competence and Levels
Determines whether the examinee has a certain level of Japanese language proficiency at the A2 level
If the total score is at or above the passing score (200 points out of 250), the applicant is assessed to have "reached a level of Japanese language proficiency to be able to engage in everyday conversation to a certain extent and handle daily life without difficulties" (A2 level). There are no level divisions for this test.
The test includes "Can-do" based questions at the A1-A2 level of the CEFR and JF Standard![]() , and comprehensively measures the Japanese language communication skills required for life situations in Japan in four sections: "Script and Vocabulary," "Conversation and Expression," "Listening Comprehension," and "Reading Comprehension". A rough indication of the A2 level is shown in the middle section of Table 2 below.
, and comprehensively measures the Japanese language communication skills required for life situations in Japan in four sections: "Script and Vocabulary," "Conversation and Expression," "Listening Comprehension," and "Reading Comprehension". A rough indication of the A2 level is shown in the middle section of Table 2 below.
| Level | Summary of linguistic competence |
|---|---|
| B1 |
|
| A2 |
|
| A1 |
|
The CEFR Global Scale: Common Reference levels
6. Test Result Notification
Test-takers will be notified of the test results as follows.
- On the day of the test
- The total score and assessment results will be displayed on the screen at the end of the test.
- Within 5 business days after taking the test
- The official notification of assessment results can be viewed and printed on the registration website after logging in.
The official notification of assessment results includes the total score and the assessment results based on the score. The total score is not simply the sum of the number of correct answers. It is a scaled score calculated using a statistical method called “equating.” The range of the total score is from 10 – 250 points. If the total score is at or above the passing score (200 points), the examinee is assessed to have reached a level of Japanese language proficiency to be able to engage in everyday conversation to a certain extent and handle daily life without difficulties. The percentage of correct answers for each section will also be included for the examinee’s reference.
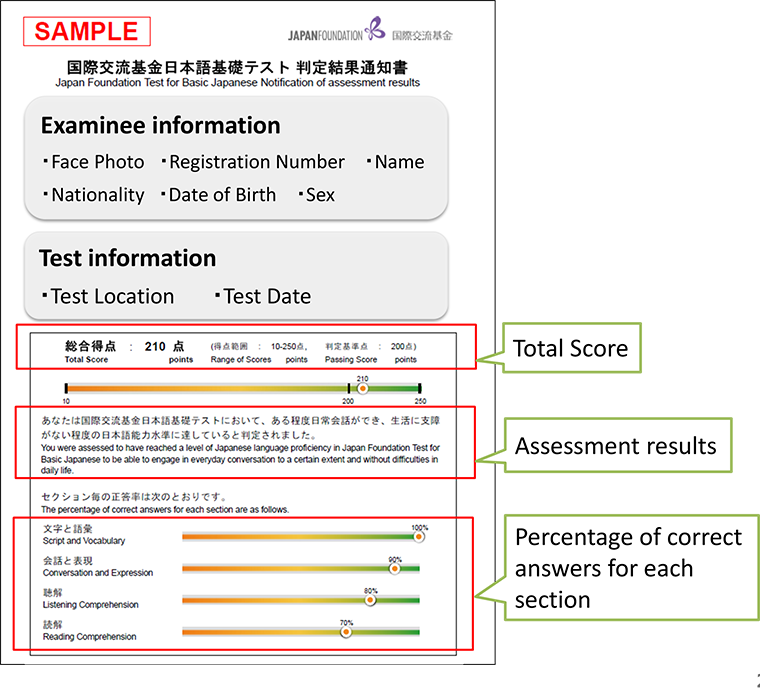
Also, the official notification of assessment describes how to view the Japanese language level on the 2nd page. Please visit “ 5.Summary of Linguistic Competence and Levels ” for contents.
7. Document Describing the Test
This is a document in slide form, which compiles the contents above and gives an overview of the JFT-Basic. It is provided in English. Please feel free to download and use it.






